
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder in men. It produces fluid that nourishes and protects sperm.
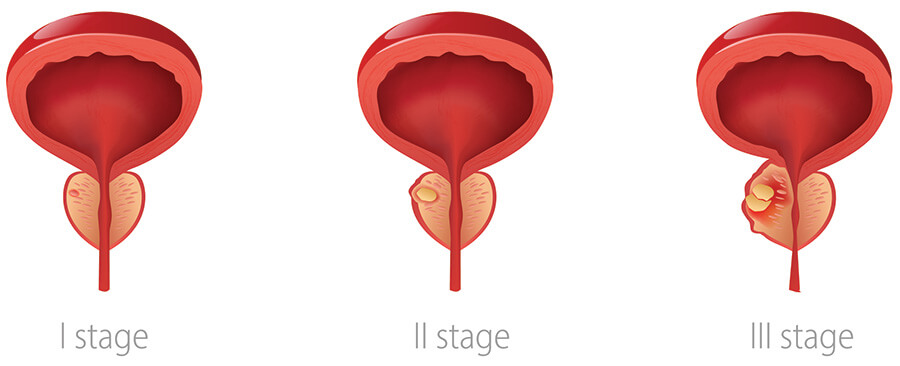
Prostate cancer begins when cells in the prostate start to grow out of control. Malignant tumors then form from these abnormal cells.
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of prostate cancer. But other forms like small cell carcinomas and sarcomas can also develop.
Some factors that raise a man’s risk of prostate cancer include:
In its early stages, prostate cancer usually has no symptoms. But some possible signs to look out for include:
Prostate cancer is often detected through screening tests before any symptoms develop. Important tests include:
If cancer is suspected, your doctor may order imaging tests like an MRI or CT scan to get a closer look at the prostate.
Early prostate cancer usually has several good treatment options:
More advanced prostate cancer may also be treated with immunotherapy or cryotherapy.
Even during and after treatment, a few things can help manage life with prostate cancer:
The key is being proactive and asking your doctor questions every step of the way. With an early diagnosis and proper treatment, prostate cancer can often be cured.